Must Read! Why Invest In Fluorspar?
*check out daily fluorspar price at fluorspar.com and fluorsparprice.com
Definition and Composition
Fluorspar, scientifically known as fluorite, is a mineral composed of calcium fluoride (CaF₂). It exhibits a cubic crystal structure and is renowned for its vibrant colors, ranging from deep purples and blues to greens and yellows. These characteristics make it both an industrial resource and a collector’s gem.
Types of Fluorspar
Fluorspar is categorized based on its purity and intended industrial application:
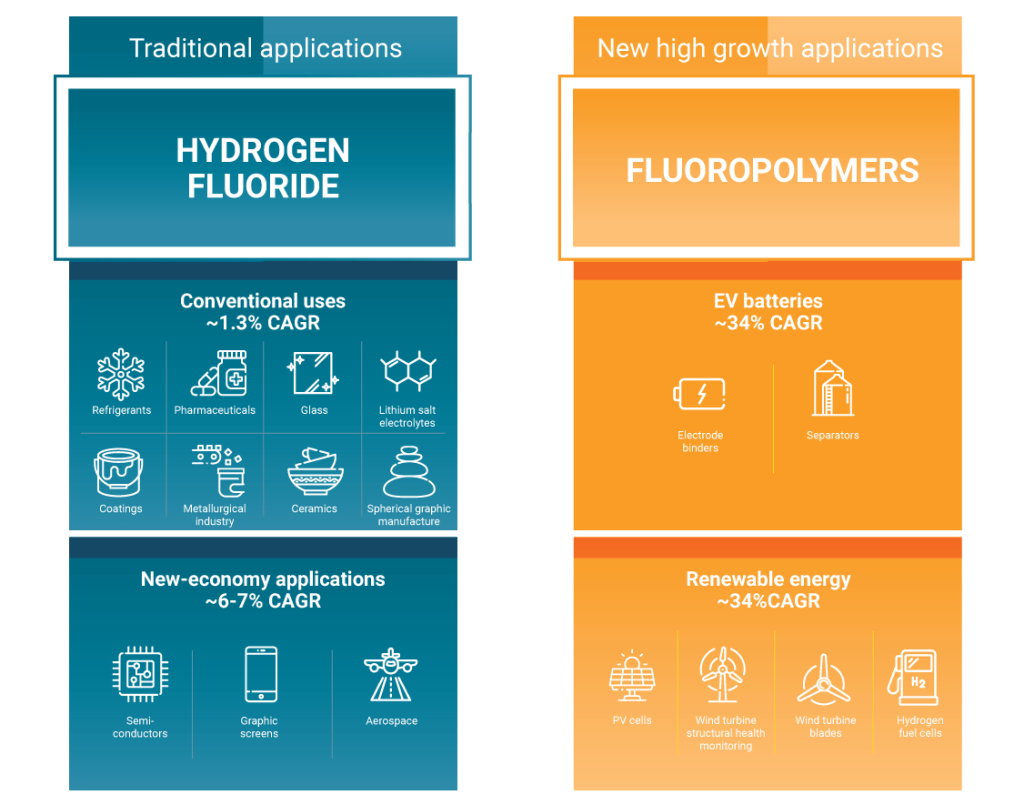
- Acid Grade: This high-purity fluorspar contains over 97% CaF₂ and is primarily utilized in the chemical industry for producing hydrofluoric acid, a precursor to various fluorine-containing compounds. Also known as Acidspar, is emerging as a key component in various stages of the battery supply chain.
- Metallurgical Grade: With a lower purity, this grade is used as a flux in steelmaking to remove impurities and enhance fluidity.
Historical Background
The term “fluorspar” originates from the Latin word “fluere,” meaning “to flow,” highlighting its early use as a flux in metal smelting to lower melting points. While ancient civilizations valued fluorspar for its decorative appeal, its industrial significance was recognized during the Industrial Revolution, notably in steel and aluminum production.
Essential Industrial Ingredient:
Fluorspar isn’t just another mineral; it’s a corner ”stone” of modern industry. It plays a vital role in the production of steel, aluminum, and glass – materials that form the backbone of our infrastructure, transportation, and everyday life. The demand for these products is only set to increase as urbanization proceeds, making fluorspar an increasingly valuable commodity.
Evolving Applications
Beyond metallurgy, the 20th century saw fluorspar’s role expand into chemical manufacturing, especially in producing hydrofluoric acid for refrigerants and fluoropolymers for high-performance coatings. Its optical properties also made it valuable in crafting lenses with minimal light dispersion for cameras and microscopes.
In the era of EV (electric vehicle) Fluorspar has shown its significance yet again as it is essential in the production of lithium-ion batteries, its content is used in all three parts of a battery. In fact, modern EV batteries like Tesla’s required roughly 10KG of fluorspar content per vehicle. These escalating demands for eco-friendly refrigerants and electronic components further underscores its significance in technological advancements.
Critical Mineral
Fluorspar plays a vital role as a strategic mineral due to its crucial applications in nuclear energy, particularly in uranium power plants. It serves as a fluxing agent in the production of uranium hexafluoride (UF6), which is a key intermediate compound in the uranium fuel cycle. By reducing the melting point of uranium oxides and facilitating their conversion into UF6, fluorspar ensures the efficient and safe operation of uranium power plants. Additionally, its unique chemical properties contribute to the extraction and purification of uranium, making it an indispensable mineral for nuclear energy production and national securityFluorspar is a vital mineral for nuclear energy production and thus critical for national security. Given its crucial role in energy-related applications., Fluorspar’s importance as a strategic mineral is set to grow.
Scarcity and Supply Constraints of Fluorspar:
Fluorspar is a relatively scarce mineral, with limited global supply. This scarcity is due to several factors:
- Geological Formation: Fluorspar is primarily found in hydrothermal veins and replacement deposits, which are relatively rare geological formations.
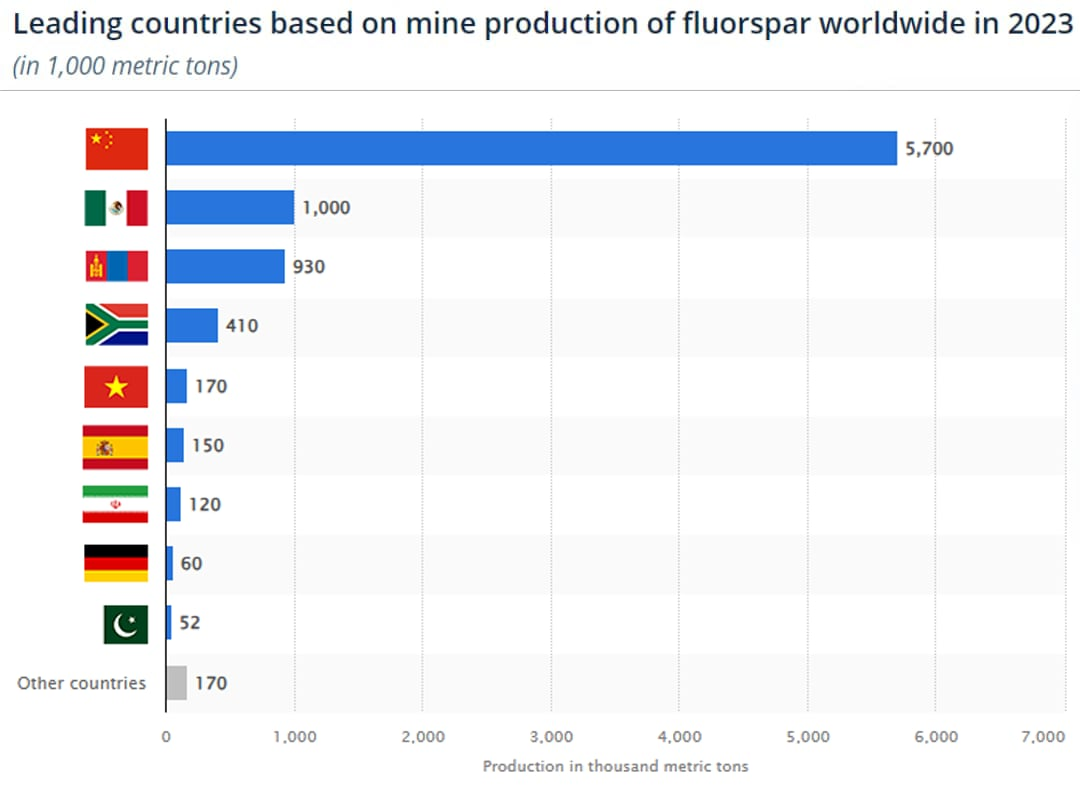
- Geographic Concentration: The majority of fluorspar reserves are concentrated in a few countries, such as China, Mexico, and Mongolia. This geographic concentration makes the supply chain vulnerable to disruptions.
- Exploration and Mining Challenges: Fluorspar deposits are often located in remote and challenging terrain, making exploration and mining difficult and expensive.
- Environmental Regulations: Stringent environmental regulations, particularly in developed countries, can make it difficult to obtain permits for fluorspar mining operations.
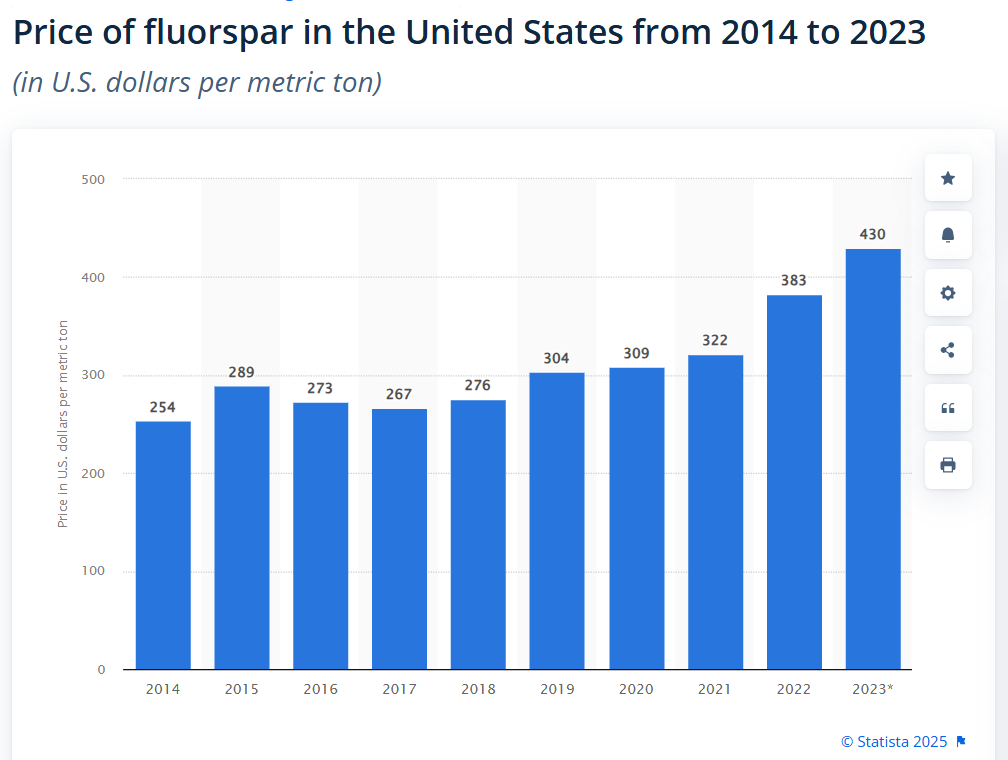
These factors have created a supply-demand imbalance for fluorspar, which is expected to drive prices upward in the coming years.
The scarcity of fluorspar and the challenges associated with its exploration and mining make it a strategic mineral of growing importance.
Why invest in Fluorspar?
With growing industrial demand and constrained supply, fluorspar prices have shown a steady upward trend. China, the largest supplier, has now turned into a net importer of fluorspar with tightened export controls, contributing to supply chain challenges. This could potentially lead to a further increase in fluorspar prices, exacerbating the supply-demand imbalance and making it a more valuable commodity. Additionally, the push for clean energy and advancements in battery technology are expected to drive long-term price growth. Investors and industries reliant on fluorspar should closely monitor market trends, as this mineral continues to be a crucial component in global industrial progress.
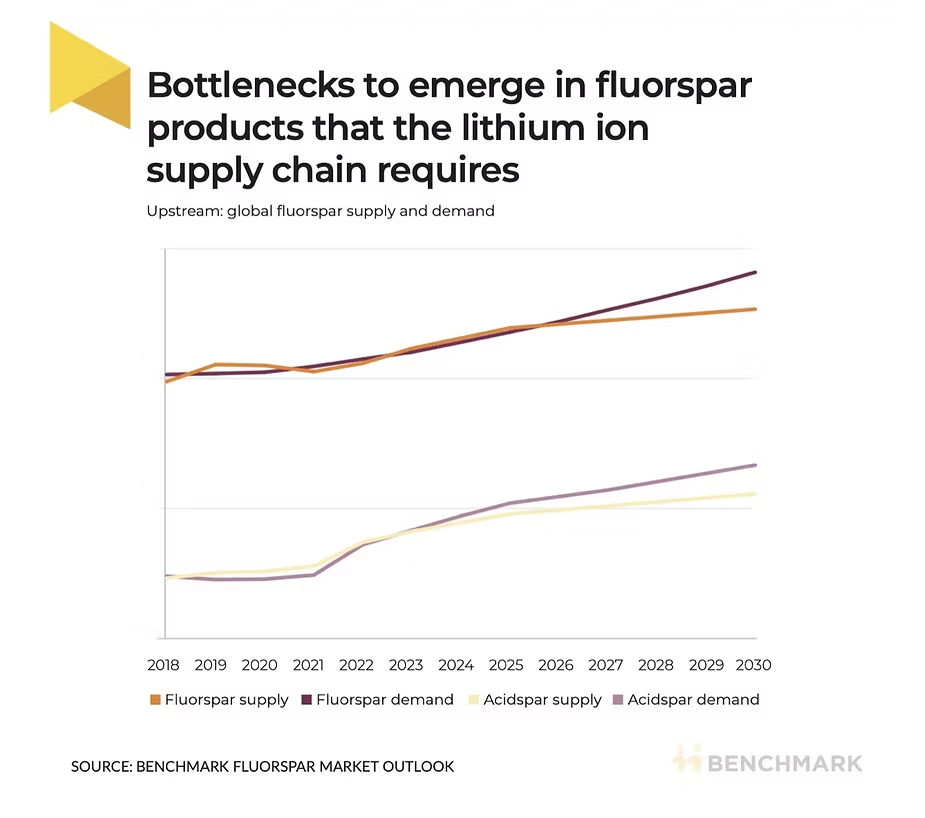
Fluorspar demand from the lithium ion battery sector is expected to exceed 1.6 million tonnes by 2030, representing a significant portion of the overall market, according to Benchmark’s Fluorspar Market Outlook.